In telecommunication, the electronic equipment that is responsible for accepting, holding, and routing telephone calls is called a “switch.” Private Branch Exchange (PBX) and Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) are switches that have different capabilities.
PBX is a switch that is kept at a designated company location and uses a specific software to handle external and internal communications. PBX uses signaling we are all familiar with such as dial tones, ringing, etc. PBX systems can also provide additional functions such as call forwarding, conference calls and reporting.
ACD is both an application and a switch and serves as the backbone of call center telephony. ACD is also known as call routing and should be able to use more sophisticated, predefined strategies to intelligently route incoming calls to the most qualified, available agent or queue.
While some PBX features can be used to mimic the more advanced ACD system by creating an organized call tree that will queue calls, some organizations need a more robust ACD package. ACD systems are typically used by call centers that handle large volumes of incoming phone calls from callers who don’t need to speak to a specific person, but need to talk someone who is available. Sometimes PBX manufacturers will provide ACD software to use as an add-on application to their system.
Below we offer an analysis describing the high-level differences between using Amtelco’s Intelligent Series (IS) ACD versus a PBX ACD with Amtelco’s call handling applications for intelligent console call centers.
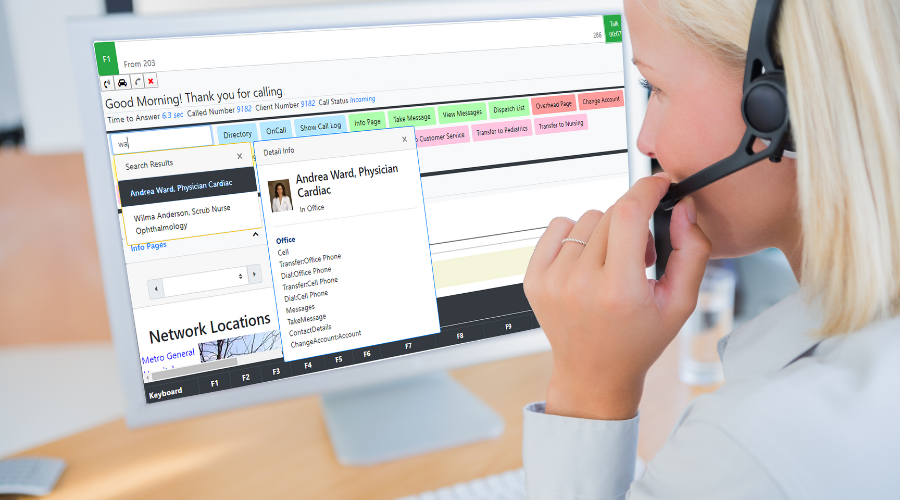
Amtelco’s Call Handling Applications
Amtelco’s Soft Agent and Web Agent applications provide the operator interface for the IS ACD. This provides seamless integration for all operator functions. Operator audio can utilize the integrated SIP softphone of Soft Agent or can be a separate PBX phone-based audio connection. The Soft Agent application functions are very similar when used with the IS ACD or with a PBX ACD.
When using a PBX ACD, the Soft Agent application provides the operator interface for PBX ACDs such as Cisco UCCX, Cisco UCCE, and Avaya CM. Soft Agent interacts with the PBX CTI interface to control the operation of a PBX phone. This enables Soft Agent to facilitate logging the agent in to the ACD, changing agent states, and processing calls – all without needing to interact with the PBX phone.
Web Agent
Web Agent is a fully functioning call handling application that performs directory searches, answer and transfer of calls, scripted messaging, dispatching, and on-call handling all with the portability of being accessible on a web browser. Web Agent turns any computer into a professional contact center agent’s workstation.
Agent styles such as dark themes, light themes, and many other visual appearances can be applied to Web Agent. These affect color, font, sizes, and icons. There isn’t a Web Agent option for a PBX ACD.
Virtual Keyboard
A virtual keyboard is available on-demand for each agent. Keyboard layouts support styles including customized keys, fore colors, and back colors. Since there isn’t a Web Agent option for a PBX ACD, the virtual keyboard is also unavailable.
Agent Status Lights
The status light plugs into the agent’s USB port on their workstation used to display a color and an effect based on the agent status. This is unavailable on a PBX ACD.
ACD
The IS ACD offers full-fledged skilled based routing schemes with multiple levels of overflow, built-in ACD queuing messages, and all-inclusive reporting. The programming of the IS ACD is very easy and is part of the IS Supervisor application along with all of the other administrative functions related
to the call center.
Operators can be assigned to ACD groups such as an intelligent console group, patient information group, code call group, etc. Calls are directed to each ACD group. If an operator is not available in a group, the calls can be set to overflow to another group or wait for an operator to become available.
Callers that are waiting to be answered can hear call queuing greetings that can be recorded for each line to customize the greeting. The greetings can also give callers the option to press a button to request a callback.
All calls are tracked and are viewable in the IS Supervisor System Monitors. This allows supervisors to monitor the activity of all calls in the system whether they are on an operator screen or waiting in queue. A supervisor viewing the system monitors can select a call-in queue and can push it to a specific
operator on demand. Supervisors can change ACD group assignments on the fly to change how calls are directed at any time without requiring operators to log off the ACD and log back in.
All calls are tracked and reported on using the IS Reporting package that is provided as part of the system.
Alternatively, a PBX ACD relies on the PBX ACD and its features and capabilities which may vary from PBX to PBX and may require purchasing additional PBX-based modules such as voice IVR (Interactive Voice Response) servers for call queuing announcements and other ancillary PBX hardware and software.
Programming PBX-based ACD requires PBX administration and typically requires involvement of telecom engineers due to the complexity of this setup. This eliminates the ability for call center staff to make changes to call routing on their own.
Automatic Number Identification (ANI) Screening
ANI Screening (blacklisting) allows screening at the system level. If the ANI of the inbound call matches the ANI or pattern that has been entered in the system, it will change to an existing account and execute the behavior of that account. It can be used for blocking robocalls.
This feature may or may not be available in the PBX ACD.
Priority Code Call Handling
The IS ACD enables special code call handling to assign priority to special calls such as code calls. The special priority allows code calls to override an operator’s normal call limit, ensuring that a code call will NEVER sit in queue.
Code call priority can also present a popup message on all operator screens whenever a code call is received, ensuring that the entire call center is aware of the call. Code call priority allows generates a special audio alert which can alert the entire call center that a code call has arrived.
Code calls can be routed through the PBX ACD but may not have the ability to generate special visual and audio alerts, or avoid being placed in queue. One of the limitations of PBX ACD’s is that they are geared towards presenting an operator with one call at a time. Going beyond one call at a time typically requires routing code calls to bridged extensions outside of the PBX ACD.
Multiple Calls
Each operator can be set for how many calls they should be able to handle simultaneously when using the IS ACD. This allows setting lower limits for less experienced operators. The operator call limit can be set to automatically change based on the current call an operator handling.
If the operator is on a code call, the operator limit can change to ensure they won’t receive any additional calls. Operator call limit and multiple call handling is critical for code calls where calls need to be handled immediately, even if all operators are currently on a call.
PBX ACDs are geared towards presenting one call at a time. Additional calls need to be routed to the operator outside of the PBX ACD to bridged appearances on the phone that are presented to the operator in Soft Agent.
Conferencing
Operators can initiate conferences to bring multiple parties together on a call. With conference join, the operators can bring in an unlimited number of parties to a call. The PBX ACD does provide conferencing capabilities and Soft Agent is able to initiate and manage PBX conferences.
Meet Me Conferencing and Patching
Operators can initiate pages to physicians to call back into the agent to be connected to a call. The agent’s ability to handle multiple calls simultaneously helps facilitate these types of calls.
PBX ACDs are geared towards presenting an agent with one call at a time. Soft Agent interacting with a PBX ACD is able to overcome these limitations by paging the physician to call the agents direct extension which typically can be presented to the agent within Soft Agent.
Voice Processing
The IS ACD’s patented integrated operator and voice processing provides a seamless connection to voice features. This allows features such as ACD call queuing messages, one button recording of calls, automated operator greetings (Perfect Answer), voice assisted transfer, callback requests from queue, and much more without having to physically move the call to an external voice processing server.
When using a PBX ACD, a call is presented to an operator on a PBX phone. To utilize voice resources, the call must be connected to a voice IVR server.
ACD Call Queuing Messages
The IS ACD and built-in voice processing enable call queuing messages to be played to callers to inform them of the status of their call. This includes custom greetings that can be recorded by each site. It includes enabling callers to exit the queue and leave a message requesting a callback if desired.
When using a PBX system, call queuing messages must be supplied by the PBX, which generally requires an additional IVR server.
Perfect Answer
Each operator can pre-record a greeting in their own voice for each phone number they answer. This reduces the repetitive answer greetings the operators need to say for each call, reducing noise and stress levels. However, pre-recorded answer greetings would need to be provided by the PBX ACD.
Call Logging
The IS ACD includes an integrated call logging solution that enables automated recording of each call the operators take, including recording of the audio, and the screen interaction recorded as a full motion video. The call log interface is an integrated part of the agent screen, enabling the agent to immediately lookup a previous call to playback the recording if there is a question about what data was gathered during the call, such as forgetting a phone number; and it is an integrated part of the IS Supervisor administrative application and part of the miTeamWeb mobile friendly web interface.
Call Logging with a PBX ACD is typically provided by a third-party solution provider.
Reporting
Event driven reporting to allow for detailed call flow reporting and custom reporting – every action that is taken for each call is recorded as an event in the reporting database. This includes ACD and operator reporting as well as paging, dialing, messaging, and on-call reporting. All reporting is integrated in a single package.
PBX reporting is used to track ACD type statistics and activities. With a PBX ACD, the PBX call activity reporting will be separate from the IS application reporting.
Paging
IS includes all paging functions in the IS server. This allows paging to be tightly integrated with operator functions as well as the built-in voice processing. IS enables users to page physicians or other staff by dialing a number and entering their call back number. This eliminates the need for an operator to be involved in every paging transaction. IS also enables users to dial a number for a specialty or department and IS will locate the person or group or people on call for that department and automatically page them. All paging activity, whether it is operator or voice activated is tracked in IS Reporting.
Voice activated paging and other voice related services is handled via an IVR system which can be supplied by Amtelco or by the PBX vendor.
Remote Operators
IS enables easy connection of remote operators using the TCP/IP LAN for data and SIP telephony or dial-up telephony connected to the IS server for operator audio. There is no need to extend PBX extensions to the remote location.
When using a PBX ACD, remote operator connectivity relies on the PBX to extend audio to a remote location.
Call Parking
Callers can be Parked to an extension within the IS ACD server. Call parking is seamlessly integrated with the operator workflow scripts.
If using a PBX ACD, the parking of callers requires the use of the PBX call parking capabilities, which may not include voice processing functions if the PBX does not support it.
After Call Work
The IS ACD can monitor an operator’s current calls and recognize a disconnected call on their screen. This allows an agent to complete their work before moving onto another call.
A PBX ACD will not recognize any call on an operator’s screen excluding a live call. When a live call is disconnected a new call will be sent to the operator. An after call work (ACW) timer can be used but will be a static amount of time between calls.
Setup – PBX Integration
Setting up trunks to an IS ACD is simple. A set number of SIP paths connect from each PBX. Specified calls are directed to these SIP endpoints. Upgrading the PBX does not change the integration as SIP is not version dependent. SIP can be used with almost any switch type/version.
With a PBX ACD, each PBX switch will need to be setup separate according to the guide provided by the manufacturer. Compatibility can be problematic.